Volume:
Paracide is a natural oral suspension for supporting a healthy intestinal environment in cattle, sheep, and poultry. Paracide contains no antibiotics and is not a prescription drug, resulting in zero milk and meat withdrawals. Paracide helps to maintain a healthy gut and digestive system with the use of natural ingredients such as clove extract, wormwood extract, glycerol and de-ionised water.
Active Ingredients: Clove Extract (Syzygium Aromaticum), Wormwood Extract (Artemisia Absinthium), Glycerol and De-Ionised Water
Target Species: Cattle, Sheep, Pigs & Poultry
Application Method: oral suspension
Application in Poultry: 100ml solution in 1000ml water daily
Withdrawal Period: zero withdrawal period in milk & meat
Doseage: 1ml solution/ 10kg bodyweight
| Body Weight | Dose Volume | Number of full doses per pack: | ||
| 1 Litre | 2.5 Litre | 5 Litre | ||
| 20 kg | 2 ml | 500 | 1250 | 2500 |
| 30 kg | 3 ml | 333 | 833 | 1666 |
| 50 kg | 5 ml | 200 | 500 | 1000 |
| 100 kg | 10 ml | 100 | 250 | 500 |
| 150 kg | 15 ml | 66 | 166 | 333 |
| 200 kg | 20 ml | 50 | 125 | 250 |
| 250 kg | 25 ml | 40 | 100 | 200 |
| 300 kg | 30 ml | 33 | 83 | 166 |
| 350 kg | 35 ml | 28 | 71 | 142 |
| 400 kg | 40 ml | 25 | 62 | 125 |
| 450 kg | 45 ml | 22 | 55 | 111 |
| 500 kg | 50 ml | 20 | 50 | 100 |
Always read the label and all enclosed information for Paracide before administering to animals!
Parasites in Cattle & Sheep
The requirement to control internal parasites will always exist as long as cattle and sheep are grazing pastures. Pastures that are heavily stocked will usually have a higher parasite burden in comparison to lightly stocked pastures. Good overall herd management, along with a successful deworming programme will improve flock and herd health, liveweight gain and milk production.
Sheep & Cattle can be infected by roundworms, tapeworms and flukes. Protozans such as coccidia are also another internal parasite that can affect sheep and cattle. There are many indicators to alert farmers of internal parasite issues within their herds and flocks. These effects are separated into subclinical and clinical effects.
| Signs and effects of infected livestock |
|
Infection: Gut Worm Symptoms: Diarrhoea, decreased appetite, loss of weight Effects: Gutworm can cause severe damage to the stomach and small intestine which will cause parasitic gastroenteritis, this will not only negatively affect the health of the animal but will affect the profitability for the farmer. |
|
Infection: Lungworm Symptoms: Short, sharp cough that becomes worse with exercise, in severe cases the animal will have obvious difficulty breathing. Effects: Lungworm infections cause a high susceptibility to respiratory viruses and bacteria. Infected cattle are prone to contracting severe bronchial pneumonia which if left untreated can lead to death. |
Key Features of Paracide:
Drench correctly
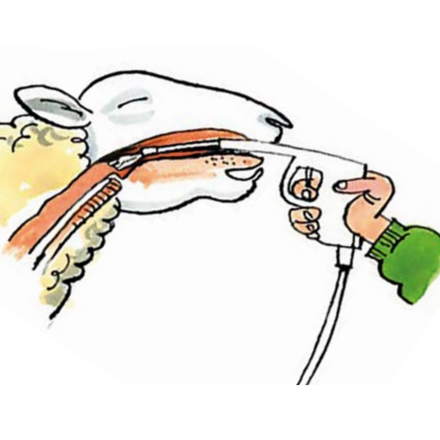
Sheep Oral Drench
The drenching technique is a vital part of ensuring that the wormer does its job effectively.
Make sure the sheep are properly restrained and cannot leap around when they are being drenched so they swallow the whole amount.
Sheep can also suffer serious injury, or even death, if they are unrestrained and the gun penetrates the tissues at the back of the mouth.
Place a hand under the head and tilt slightly to the side.
Slot the nozzle in the gap between molar and incisor teeth and then over the back of the tongue.
If the wormer is just put into the mouth, it will bypass the rumen as it escapes down the oesophageal groove and will be less effective.
This is particularly important for white (BZ) drenches.
Dosing Weight – do not guess. Underestimating the weight of an animal is a common cause of underdosing.
Select and weigh the biggest animal in the group to determine the correct dose.
If there is a wide range of weights, consider splitting the group, then weigh the heaviest in each section.
Do not forget to check that the weigh crate is accurate before starting!
Calibrate and maintain the drench gun
Always check the gun is delivering the right amount before you drench.
Remove the plunger from a 10 ml syringe, put a thumb over the end and squirt the dose into it, making sure there are no air bubbles left.
Adjust the gun until the dose delivered is correct.
Drenching guns should also be well maintained and replaced regularly.
Clean with warm soapy water after use and check springs and tubes to make sure there are no kinks that will form air bubbles.
Withholding food
Research has shown that the efficacy of the white (BZ) and clear (AV) drenches can be improved by withholding food for 12–24 hours before treatment.
It is not advised to deprive heavily pregnant ewes of food, so if you treat this class of stock with anthelmintics, you may wish to use yellow drenches (LV) because their efficacy is less dependent on rumen fill.
Storage
Wormers should be stored securely, away from direct sunlight at 4–25°C.
Check the use-by date and, once open, use within the time shown on the packaging.
Shake white (BZ) products well before use.
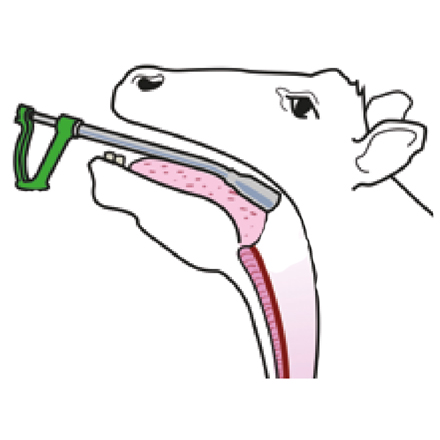
Cattle Oral drenches
Oral drenching guns are designed to deliver the treatment towards the back of the mouth over the tongue, so the entire dose is swallowed at once to optimise efficacy.
• Make sure animals are properly restrained, with their head held up
• Slide the nozzle of the dosing gun in the side of the mouth and over the tongue so that the entire dose is swallowed immediately
• Drenching equipment must be correctly calibrated and in good working order
• Calibrate the gun using the product just before treatment starts by delivering two or more doses into a graduated measuring cylinder.
Faulty equipment, or attempting to dose too quickly, may mean that the barrel of the gun does not fill properly or that the liquid is full of bubbles.

Would you like to send this voucher to the recipient via email?
Yes No